Long-term sleep disorders worsen well-being, spoil mood, reduce efficiency in all areas of life, so the demand for sleeping pills is always very high. Not all people are ready to turn to a somnologist or therapist to find out the reasons for their insomnia: someone does not trust modern healthcare, and someone simply does not have time to visit a doctor. The question arises: what sleeping pills are available without a prescription?
Drugs for the treatment of insomnia are presented in different dosage forms
There is another side to the issue: for some people, due to a number of reasons (for example, exacerbation of peptic ulcer disease), preparations in the form of capsules or tablets are contraindicated. They require sleeping pills in solution in ampoule form for intramuscular or intravenous injection. What medicines are on the pharmaceutical market? Is it possible to purchase them without a doctor's prescription? What are the pitfalls?
Intramuscular sleep
Since ampoules usually contain a potent sleeping pill, the dispensing of such drugs is carried out exclusively by prescription. Possible side effects, the risk of overdose or the formation of drug dependence are all reasons to regulate the circulation of such drugs in the Russian Federation.
If you want to purchase sleeping pills in ampoule form without a prescription, then perhaps the only option is Diphenhydramine. This drug is inexpensive, up to 80 rubles. Since its main purpose is antihistamine, and it was banned only recently, you may be sold in some pharmacies where vacation conditions are not given too much great importance... However, it is best to see a doctor who will write you a prescription for this drug.
Since it is very dangerous to use a potent sleeping pill without a doctor's supervision, the Ministry of Health regulates the circulation of the following drugs in the Russian Federation, which you can purchase with a prescription:
- Flormidal;
- Rohypnol;
- Gemenevrin;
- Dormikum.

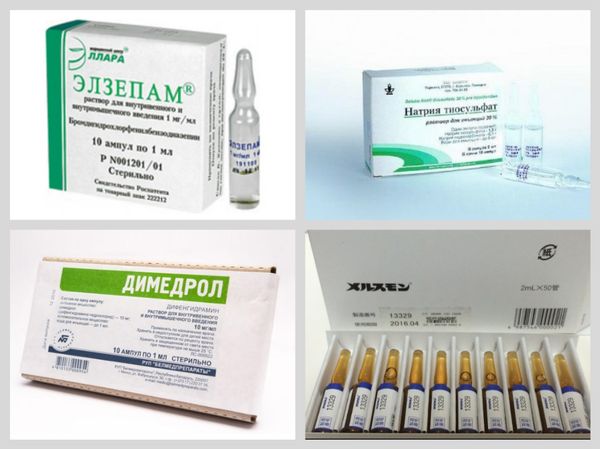
Sleeping pills in ampoules
All these hypnotics are very powerful, most often they are prescribed in clinical cases of delirium (alcoholic hallucinations), severe anxiety disorders. Sometimes they are used as anesthesia, and it is very important to accurately select the dose, especially if the patient is elderly or has chronic diseases. Sleeping pills in ampoules most often belong to the group of benzodiazepines, although Gemeneurin is a psycholeptic.
Be aware that powerful sedatives can have serious side effects. They are contraindicated in people suffering from sleep apnea who have serious chronic diseases of the kidneys, liver, and should be prescribed exclusively by a doctor after a comprehensive examination!
A sound sleep without a prescription
The circulation of powerful sedatives is controlled by the state, since many of them have a number of unpleasant side effects(up to the cessation of breathing during sleep), and also cause addiction. Only a doctor should prescribe such drugs after a full examination, and their use should be as careful as possible. Over-the-counter sleeping pills are available to combat everyday insomnia. Most often, they are enough to cope with nervous irritability before bedtime.
Please note that the effectiveness of the action of one or another sleeping pill is achieved due to its competent selection in accordance with the type of insomnia and the individual characteristics of the patient. A person who has difficulty falling asleep does not need a potent sedative at all, it is enough to overcome the threshold of immersion in slow sleep. If the problem is related to the depth of sleep or frequent awakenings, then long-acting agents are prescribed.

Drugs for the treatment of insomnia
Among hypnotics over-the-counter are three groups:
- Herbal medicines, herbal preparations, infusions.
- Hormonal agents.
- H1-histamine receptor blockers.
Herbal preparations
The following herbs are used to provide a sedative effect: mint, lemon balm, valerian, hops, lavender, thyme. You can buy dried herbs, then prepare the infusion yourself, or you can buy ready-made tablets with extracts, for example, Persen or Novo-passit. They drink them in a course of 2-3 weeks. Synthetic remedies are much stronger, however, it is natural herbal remedies that help to cope with mild insomnia without side effects. Some of the herbs can be used by children, but before that, be sure to consult a pediatrician.
If you have never been bothered by insomnia, you should start with herbal infusions. They are the safest over-the-counter sleeping pills. Herbal preparations have a calming effect by naturally preparing the body for sleep. Herbs are safe and do not interfere with sleep patterns, so use them before resorting to serious medications.
Hormonal drugs
The sleepiness people feel at night is due to the sleep hormone melatonin, which is produced at night and in dark time days. Taking advantage of this feature of our body, scientists have developed a synthetic agent that, when taken orally, increases the level of this hormone in humans. Under the influence of melatonin, the body relaxes, muscle tone decreases, it becomes easier to abstract from external stimuli that prevent comfortable falling asleep.
In pharmacies, this medicine is called Melaxen. It is sold freely, without a prescription, since it has no side effects, and an overdose after taking it is almost impossible. It is not addictive and is often used by people who have to change time zones and adapt to a new regime of day and night.
Histamine receptor blockers
Not all drugs in this group are released freely, but among them there is one that is used in ampoules - Diphenhydramine. Most commonly, histamine receptor blocking drugs are used to suppress allergy symptoms, but due to their sedative effects, they are also prescribed as sleeping pills. They do not cause drowsiness during the day and have a duration of 8 hours. Improves the quality of sleep, its depth, without exerting negative impact for the morning well-being.
There are a number of side effects: burning eyes, dry mouth, dehydration, and constipation as a result. The body temperature may rise, sometimes there are visual impairments. Frequent use of drugs in this group increases the risk of side effects, so long-term use is not recommended. Better to fight insomnia with milder means.
Ampoule sedatives for animals without a prescription

Injectable sleeping pills for animals
There are also injectable sleeping pills for animals. They are available without a prescription, freely available through veterinary clinics, and can be used for preoperative anesthesia or as a sedative during transport. If you need your pet to sleep for several hours, the following medications can be used:
- Vetranquil 1% is a sedative muscle relaxant. The duration is one hour. For short-term euthanasia of animals before, for example, a veterinarian examination.
- Zoletil is a drug used for anesthesia. It has an analgesic effect, a short-term anesthetic effect. Used before minor surgery.
- KsilaVet is a sleeping pill before examination or X-ray. Immobilizes active animals for vaccination or suturing.
In humans, insomnia develops from many reasons: with neuroses, other nervous and mental illness, on the basis of pain, with improper organization of the daily regimen, mental fatigue.
Sleep pills are drugs that promote normal sleep. Since for a hypnotic effect it is necessary to achieve only the most initial stage oppression of the central nervous system, then drugs from various chemical and pharmacological groups are used as hypnotics. So, sedative drugs enhance the inhibition process or lower the excitation process, that is, they regulate the functions of the central nervous system, including sleep. Antipsychotics are substances with sedative and antipsychotic properties. Tranquilizers are drugs of a sedative effect, due to which they weaken the manifestations of neurotic conditions.
Barbiturates. Barbituric acid itself does not have a hypnotic effect, but its derivatives, obtained by replacing hydrogen atoms with various organic radicals, have this ability. Different barbiturates have different duration of action, which is associated with the peculiarities of their transformation in the body and excretion from it. Long-acting barbiturates include: barbital, sodium barbital, phenobarbital (luminal); to drugs average duration actions - barmamil, sodium ethaminal (nembutal), cyclobarbital; short-acting drugs - hexobarbital.
The routes of administration of barbiturates are different: oral, intramuscular, intravenous, rectal. The choice of barbiturate and the route of its administration depend on the indications and the solubility of the drug. If the patient falls asleep easily, but wakes up early, then drugs with a long-term effect (barbital, sodium barbital) are prescribed. If the patient only falls asleep with difficulty, then short-acting drugs are used. Rectal barbiturates are prescribed to agitated patients and for induction of anesthesia. When administered intramuscularly, the effect occurs faster.
Long-acting barbiturates are excreted from the body mainly by the kidneys, while short-acting barbiturates are destroyed mainly in the liver. In liver diseases, the use of barbiturates (especially short-acting ones) is contraindicated. It should be borne in mind that analgesics and antipsychotics can potentiate the action of barbiturates; with prolonged use, addiction can develop. In some cases, there is an increased sensitivity to barbiturates and an unusual reaction - excitement. Skin allergic reactions may also occur. When using barbiturates for pain relief during labor, it must be borne in mind that they relatively easily pass through the placental barrier and pass into the mother's milk.
Barbital(veronal) refers to long-acting barbiturates. It induces deep, sustained sleep. Side effects: weakness, nausea, vomiting, headache; the drug is addictive. Assign orally at a dose of 0.3-0.5 g for adults 0.5-1 hours before bedtime, for children - from 0.025 to 0.25 g, depending on age. Contraindications: severe liver and kidney disease. Release form: tablets of 0.3-0.5 g.
Sodium barbital(medinal, veronal sodium), due to its good solubility, has a hypnotic and sedative effect somewhat faster than barbital. In addition, it is eliminated from the body faster and is less toxic. Used for insomnia, nervous excitement, neuralgia, sometimes as an antiemetic and anticonvulsant. Assign inside 0.3-0.5-0.75 g, children, depending on age, 0.025 - 0.25 g per dose. How is sleeping pill mistaken for? - 1 hour before bedtime, washed down with warm tea. The highest single dose is 0.5 g, the highest daily dose is 1 g. Method of production: tablets of 0.3 g, ampoules of 5 ml of 10% solution. Contraindications: liver and kidney disease with severe impairment of excretory function.
Phenobarbital(luminal) has a sedative, hypnotic and pronounced anticonvulsant effect. It is used for insomnia, hyperexcitability, epilepsy, chorea, spastic paralysis, the initial stage of hypertension in combination with antispasmodics. Inside it is prescribed as a hypnotic and sedative 0.01-0.05 g 2-3 times a day, with epilepsy - 0.05 g once a day with an increase in the dose of 0.025 g per day. The highest single dose is 0.2 g, the highest daily dose is 0.5 g. Side effects: headache, gait disturbances, with prolonged use - addiction. The contraindications are the same. Release form: tablets of 0.05-0.1 g. There are also combined tablets in combination with papaverine, salsolin, dibazol and other antispasmodics, as well as with analgesics.
Barbamil(amytal sodium) has a hypnotic, sedative and anticonvulsant effect. Used for various types of insomnia, psychotropic agitation, epilepsy. Assign inside before going to bed, 0.1 - 0.2 g, children - 0.01 - 0.015 g; with a sharp excitement, 5-10 ml of a 5% solution is injected intramuscularly, 5-10 ml of a 5% solution intravenously at a rate of 1 ml per minute or in enemas. With epilepsy, 0.025-0.05 g is given orally 2 to 3 times a day. With prolonged use, barbamil is addictive. Release form: tablets of 0.1 - 0.2 g.
Etaminal sodium(nembutal). In action it is close to barbamil, but it breaks down, however, somewhat faster and acts for a shorter period of time. In some cases, the drug is better tolerated than barbamil. It is used for various types of insomnia. Assign orally to 0.1-0.2 g, children - 0.01-0.1 g rectally in suppositories and enemas, 0.2-0.3 g, intravenously - 5-10 ml of 5% solution. The highest single dose is 0.3, the highest daily dose is 0.6 g. Contraindications: liver and kidney disease with impaired excretory function. Release form: tablets of 0.1 g.
Cyclobarbital(fanodorm) in pharmacological action is close to barbamil, sodium etaminal. Sleep usually lasts 5-7 hours. It is used for sleep disorders of various etiologies. In states of arousal, neurasthenic syndrome, it is used as a sedative. Assign inside as a sleeping pill half an hour before bedtime at OD-0.2 g. Side effects: with poor tolerance or overdose - headache, dizziness, sometimes allergic reactions. The drug is addictive. Contraindications: severe liver pathology. Release form: tablets of 0.2 g.
Hexobarbital(barbidorm) in chemical structure and pharmacological properties is close to hexenal; the drug is rapidly absorbed and has a hypnotic effect 15-30 minutes after ingestion for 4-5 hours. Assign inside 0.25-0.5 g. The highest single dose is 0.5 g; the highest daily allowance is 1g. Side effects: nausea, vomiting, headache, with prolonged use - addiction. The contraindications are the same. Release form: tablets of 0.25 g.
In search of sleeping pills, deprived side effects barbiturates, drugs from other chemical groups have been synthesized.
Tetridine(benedorm). In terms of chemical structure, it has some similarities with barbiturates, however, tetridine is low-toxic, in hypnotic doses it does not significantly affect respiration and blood circulation and is almost not addictive. Assign inside for various types of insomnia, neurasthenic disorders, 0.2-0.4 g in pure form and in combination with other hypnotics, including barbiturates. The highest single dose is 0.5 g, the highest daily dose is 1.5 g. Side effects: overdose and hypersensitivity may cause nausea, weakness, headache. Release form: tablets of 0.2 g.
Noxiron less active than barbiturates. Used mainly for neurotic conditions. Sleep occurs in 15 - 30 minutes and lasts 6-8 hours. For insomnia, including in elderly people, 0.1-0.25 g each is prescribed as a sedative, 0.25 g each as a sleeping pill. 0.5 g. Side effects are rare. The possibility of allergic complications should be taken into account; with prolonged use, noxiron is addictive. Release form: tablets of 0.25 g.
Chloral hydrate, a hypnotic of the aliphatic series, has a sedative, hypnotic and analgesic effect, and in large doses - narcotic. Used as a sedative, hypnotic and anticonvulsant for spasmophilia, tetanus, eclampsia. Assign inside 0.2-1.0 g, in enemas with enveloping substances (due to the irritating effect on the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines). The highest single dose is 2.0 g, the highest daily dose is 6.0 g. Side effects: in case of an overdose - vomiting, a drop in blood pressure, with prolonged use - addiction. Release form: powder and tablets of 0.5 - 0.75 and 1.5 g.
Carbromal(adaline) has a sedative and mild hypnotic effect. Applied for neurasthenia inward, 0.3-0.5 g (as a sleeping pill 1 hour before sleep). The highest single dose is 1 g, the highest daily dose is 2 g. Contraindications: idiosyncrasy to bromine preparations (bromism). Release form: tablets of 0.5 g.
Bromized(bromural) has a sedative and mild hypnotic effect. Used for insomnia, nervous excitement. Assign inside as a sedative 0.3-0.6 g 2 times a day, as a sleeping pill - 0.6 g 30-40 minutes before bedtime. Contraindication: idiosyncrasy to bromine preparations. Release form: tablets of 0.3 g.
Sodium bromide- a sedative with the ability to enhance the processes of inhibition in the cerebral cortex. Bromine preparations are used for neurasthenia, neurosis, hysteria, increased irritability, insomnia, epilepsy, and chorea. Sodium bromide is prescribed orally in solutions (in mixtures), tablets, and also intravenously. Inside appoint 0.1 - 1 g 3-4 times a day; children, depending on age - from 0.05 to 0.4 g. With prolonged use of bromides, side effects (bromism) are possible: runny nose, cough, conjunctivitis, general weakness, skin rash. In these cases, sodium chloride is administered in large doses (10-25 g per day) in combination with a large amount of water (3-5 liters per day). Release form: powder and tablets of 0.15 - 0.5 g. Store in a dark place.
Rhizome with valerian roots contain 0.5-2% essential oil, free valeric acid and borneol, alkaloids (valerin, hatinine), tannins, and sugars. Valerian preparations reduce the excitability of the central nervous system and have a moderate antispasmodic effect. Indications for use: hyperexcitability, insomnia, neuroses of the cardiovascular system, spasm of the gastrointestinal tract. Assign root infusion inside - 6 - 10 g per 180-200 ml of water - 1 tablespoon 3-4 times a day; tincture - 20-30 drops 3-4 times a day; valerian extract thick in tablets - 0.02 - 0.04 g per dose. Release form: rhizome with valerian roots 100 g each or 75 g briquettes, valerian tincture in 30 ml vials, thick extract in tablets 0.02 g each.
Collection sedative... Ingredients: peppermint leaves 2 parts, water trefoil leaves 2 parts, rhizomes with valerian roots 1 part, hop infructescence 1 part. It is used for increased excitability, insomnia in the form of an infusion (2 tablespoons per glass of boiling water, half a glass 2 times a day).
Motherwort herb contains essential oil, saponins, tannins, alkaloids. It is prescribed in the form of an infusion, tincture or extract as a sedative for increased excitability, cardiovascular neuroses, in the early stage of hypertension. Sometimes used as a collection with valerian roots, caraway and fennel fruits. To prepare the infusion, take 15 g of grass per 200 ml of water. The tincture is available in bottles of 25-30 ml, it is taken in 30-50 drops 3-4 times a day.
Corvalol- a combined preparation containing 2% ethyl ester of alpha-bromo-isovaleric acid, 1.83% phenobarbital, 7.9% 1 N. caustic soda solution, 0.14% mint oil, a mixture of 96% alcohol and water - up to 100%. Caustic soda is added to convert phenobarbital to soluble sodium phenobarbital. The composition and action is similar to the drug valocordin (2% phenobarbital, 2% ethyl ester of alpha-bromisovaleric acid, 0.14% mint oil, 0.02% hop oil, a mixture of 96% alcohol and water - up to 100%). It is used for neuroses, increased irritability, spasms of the coronary vessels, tachycardia, insomnia, early stages of hypertension, intestinal spasms. Prescribe 15-20 drops, with tachycardia - 30-40 drops several times a day. Release form: bottles of 15 ml.
Thioridazine(Sonapax, Melleril) - antipsychotic; it is used for neuroses, acute and subacute schizophrenia, organic psychosis. With increased excitability, neuroses, anxiety, appoint 0.005-0.01 g 30-40 minutes before bedtime. Contraindications: coma, allergic reactions, glaucoma. Release form: dragees of 0.01, 0.025 and 0.1 g. In children's practice, a 2% suspension is used.
Meprotan(andaxin, meprobamate) is a tranquilizer, it has a calming effect on the central nervous system, enhances the effect of hypnotics, relieves emotional stress, alarming. Assign inside 0.2-0.4 g 2 - 3 times a day, if necessary, the dose is increased to 2-3 g per day. As a sleeping pill, use 0.2-0.4 g half an hour before bedtime. The highest single dose is 0.8 g, the highest daily dose is 3.0 g. Side effects: in some cases, skin rashes, dienia. Contraindication: work requiring a quick mental and motor reaction.
Chlordiazepoxide(elenium, librium, napoton) has a calming effect on the central nervous system, causes muscle relaxation (decrease muscle tone). Used for neurotic reactions and mental illnesses with neurosis-like disorders, for premedication in surgery. Assign inside 0.005-0.01 g 2-4 times a day. Side effects: dizziness, itching, nausea, constipation. Contraindications: severe kidney and liver disease; myasthenia gravis.
Diazepam(seduxen) in structure and pharmacological properties is close to Elenium. Has a calming effect on the central nervous system, has a muscle relaxant effect. In case of neuroses, it is prescribed orally at 0.005-0.01 g, if necessary, 2 ml of a 0.5% solution intramuscularly. Side effects: slight dizziness, itching, constipation. Contraindications: myasthenia gravis, work requiring a quick mental and motor reaction. Release form: tablets of 0.005 g, ampoules of 2 ml of 5% solution.
Oxazepam(tazepam) has a calming effect on the central nervous system, similar in action to seduxen and elenium. Used for neuroses and neurosis-like conditions, accompanied by fear, anxiety, insomnia. Assign inside 0.01 g 3-4 times a day. Side effects: dry mouth, lethargy, sometimes agitation, ataxia, disorder of accommodation. Contraindications: acute diseases of the liver and kidneys, myasthenia gravis, work at height, at moving mechanisms and driving a car. Release form: tablets of 0.01 g.
Nitrazepam(eunoktin, radedorm). The hypnotic effect of the drug is mainly associated with a decrease in emotional excitability. It promotes and deepens physiological sleep. It is used as a hypnotic for sleep disturbances of various etiologies. Sleep occurs in 20-45 minutes and lasts 6-8 hours. Assign inside 0.0025-0.01 g 30-40 minutes before bedtime. Side effects: sometimes dizziness, itching, nausea. Contraindications: myasthenia gravis, pregnancy, should not be prescribed to transport drivers. Release form: tablets of 0.01 g.
Oxylidine is a sedative, it reduces the excitability of the central nervous system, enhances the effect of hypnotics, narcotics and analgesics. Used for psychopathy, neuroses, sleep disorders of various etiologies. Assign inside 0.02-0.06 g, intramuscularly 1 ml of 2% solution. Side effects: with increased sensitivity, dry mouth, nausea, polyuria, skin rashes are possible. Contraindications: arterial hypotension, severe kidney disease. Release form: tablets of 0.02 g, ampoules of 1 ml of 2 and 5% solutions.
Trioxazine- a tranquilizing agent, devoid of muscle relaxant effect. Calms the central nervous system. Used for neurotic conditions, insomnia, irritability, fatigue. Assign inside 0.3 g 2-3 times a day. Side effects: dry mouth, lethargy, weakness, nausea. Release form: tablets of 0.3 g.
Fruticin has a calming effect on the central nervous system, also has cardiotonic activity. It is used as a sedative for vegetative neuroses, neuroses of the cardiovascular system, paroxysmal tachycardia. Assign inside 0.05 g. The drug is usually well tolerated. Release form: tablets of 0.05 g.
Gindarin has a tranquilizing effect. It is used for increased excitability of the nervous system, neurasthenia, insomnia. Assign inside 0.05-0.075 g 2 - 3 times a day.
It has been established that a certain natural hypnotic substance is formed in the body, due to the entry of which into the blood a person falls asleep. The basis for this statement was the isolation of a similar substance from the blood of a sleeping rabbit. Perhaps, on its basis, hypnotics will be created, devoid of side effects.
Insomnia is a scourge modern man who is constantly in a hurry somewhere, is late, works at the limit of his strength, often does not even have enough time to sleep. And if the quality of sleep also fails and the cause of the disorder cannot be eliminated in any other way, you have to resort to the use of hypnotics in various forms.
The most potent hypnotics are limited supply and require a prescription.
Sleep aids are drugs that potentiate falling asleep and / or normalize the depth and duration of sleep in the presence of such disorders. Sleeping pills are constantly taken by 3% of the world's population, periodically ─ about a quarter, in addition, the frequency of their use increases with age.
Sleep disturbances
Possible different kinds sleep disorders, depending on this, the desired drug will be selected. There may be the following problems:
- Difficulty falling asleep. Short-acting hypnotics are used to "put" a person to sleep.
- Frequent waking up at night, shallow sleep. The structure of sleep is disturbed: the fast phase prevails over the slow one. This will require a long-term remedy that will correct this imbalance.
- Superficial sleep and early awakenings. Most often observed in the elderly in connection with atherosclerotic changes in the vessels of the brain. In this case, hypnotics with a short (upon awakening) and long (taken in the evening, before bedtime) duration of action are effective.
Classification
Preparations produced in injectable forms:
- Benzodiazepine derivatives:
- Elzepam: in ampoules of 1 and 2 ml for intramuscular administration,
- Flunitrazepam: 1 ml ampoules.
- Derivatives of gamma-aminobutyric acid:
- Sodium oxybutyrate: 10 ml ampoules.
- Barbiturates:
- Phenobarbital: 2 ml ampoules.
- Etaminal sodium: 1 ml ampoules.
- Antihistamines:
- Diphenhydramine: 1 ml ampoules.
- Epithalamin: 1 ml ampoules.
All injectables are available with a doctor's prescription.
Hypnotics act primarily on the central nervous system
Drugs ─ benzodiazepine derivatives
They enhance the effect of the main inhibitory mediator in the nervous system, gamma-aminobutyric acid, by binding to receptors intended for this neurotransmitter and simulating its effect.
They have hypnotic, anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) and anticonvulsant effects.
Side effects: a sharp severity of postsomnicheskoy syndrome, withdrawal syndrome, increase the effect of alcohol, which, if inadvertently combined with it, can cause respiratory failure and even provoke respiratory arrest.
Against the background of long-term use of drugs, the so-called "recoil" syndrome may occur, although when using this group of drugs, it rarely occurs ─ this side effect is more typical for the use of barbiturates.
These are new selective hypnotics that interact with a limited number of receptors in the nervous system, and therefore the side effects are not so pronounced.
They do not have the ability to accumulate.
These drugs do not interfere with sleep patterns and are therefore well tolerated.
Side effects: low anxiolytic and anticonvulsant effects, withdrawal syndrome.
The drugs should not be used when breastfeeding, otherwise the child may experience disorders of the nervous system, including withdrawal syndrome.

Cyclopirrolones and imidazopyridines are considered the most modern drugs(3rd generation).
Derivatives of GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
Directly stimulate gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors in the central nervous system.
With the help of these drugs, it is possible to achieve various degrees of inhibition of the functions of the nervous system ─ from sedation and hypnotic effects, to the introduction of general anesthesia.
Reversibly inhibit the excitability of receptors in all body tissues, including the central nervous system. At low doses, barbiturates facilitate the action of GABA on its receptors; at high doses, barbiturates themselves stimulate its receptors by binding to them instead. In addition, they block the action of activating substances-mediators, such as aspartate and glutamate, slow down the release of acetylcholine from their receptors.
Along with the hypnotic effect, derivatives of barbituric acid significantly alter the very structure of sleep. At the same time, the proportion of "REM sleep" decreases, the phase of "slow sleep" increases.
The undesirable effects of barbiturates are significant:
- Aftereffect: lethargy and drowsiness, lack of coordination and weakness during the day. Some patients may experience irritation, manifestations of aggression (as a result of the phenomenon of drug accumulation in the central nervous system).
- The syndrome of "recoil" can occur even after just a few days of using drugs of this pharmacological group. At the same time, insomnia becomes even more pronounced than before treatment, the patient is irritated, does not feel rest. The proportion of the phase of "REM sleep" sharply increases, sleep becomes superficial and shallow, the number of episodes of awakening at night increases.
- Addiction and dependence. With long-term use of drugs, you have to gradually increase their dosage, since the effect of them decreases due to the addictive effect (more enzymes are produced in the body that destroy the sleeping pill). After 2 weeks of use, mental and physical dependence on the use of barbiturates develops.
- Dosage features. An overdose can very quickly cause deep anesthesia and even respiratory arrest.
Barbiturates and Benzodiazepines - drugs with long-term hypnotic effects
Antihistamines
Reduce the phase of "REM sleep". The hypnotic effect is rather weak, they quickly lose their effectiveness with prolonged use. They cause an aftereffect: daytime sleepiness, absent-mindedness, impaired coordination.
Melatonin is normally produced in our body and serves as a regulator of the rhythms of sleep and wakefulness. Drugs that have a melatonin-like effect on the receptors of the nervous system are effective, for example, when the pineal gland (pineal gland) is deficient, which normally secretes this hormone. They can also be used after discontinuation of benzodiazepine drugs.
Problems with the use of sleeping pills
In medicine, there are some problems regarding hypnotics (or hypnotics), namely:
- A significant number of unwanted effects.
- Lack of strict criteria for choosing a particular drug for treatment in each case.
When using sleeping pills, the morning appearance of the so-called post-somnic syndrome is common, the manifestations of which are:
- Weakness, lethargy.
- Heaviness in the head and headaches.
- Drowsiness.
- Irritability.
- Reduced focus.

The body relaxes under the influence of melatonin and muscle tone decreases
Conclusion
Sleeping pills in ampoules should only be used as directed by a doctor, regardless of whether it is available with or without a prescription. Injection forms are generally not very popular for everyday use hypnotics. Most often prescribed for:
- The severe general condition of the patient due to his underlying disease.
- The onset of acute psychoses with impaired consciousness (delirium, hallucinations).
- General anesthesia as a component.
- Anticonvulsant therapy.
You should not start using any sleeping pills on your own.
In case of sleep disorders, first of all, you need to see a doctor to find out the reasons. The doctor will send for a polysomnographic study, according to the results of which he will determine the need to use hypnotics, if necessary, he will prescribe a certain drug.
The causes of insomnia can be very different, finding out them will help solve the problem once and for all and without the use of drugs that can harm the patient, since they have many side effects and can cause addiction, and many sleeping pills change the structure of sleep.
For example, if insomnia is caused by depression, then hypnotics in this case will affect the effect, not the cause. You need to do first of all psychological state, then sleep will return to normal.











Characteristics of the hero Grushnitsky, Hero of our time, Lermontov
Analysis of the play "The Inspector General" (N
Melekhov's image as a continuation of the traditions of Russian literature
When gerasim painted a picture after the rain
Prince Vasily (War and Peace)