Sputum is a tracheobronchial secret, consisting of a mixture of saliva, mucus from the nose and substances that have fallen from the outside with the air. Mucus in the nose is necessary to protect the respiratory tract from drying out and the penetration of pathogens with air. If inflammation or allergies still occur, the secret becomes thicker, so it accumulates and it becomes quite difficult to get rid of it.
Why does mucus accumulate in the throat?
The accumulation of mucus in the throat is the most common complaint that ENT doctors hear. It indicates the disrupted work of glandular tissues and ciliated epithelium. Provocateurs of these processes can be bacteria, viruses, fungal infections or substances that cause allergies.
Due to inflammation in the upper or lower body of the respiratory system, goblet cells are stimulated, which produce more mucus. It is her excess that can accumulate in the throat, as well as in the bronchi and when draining down the throat, cause considerable discomfort.
Why is mucus not coughed up?
For the above reasons, the secret accumulates, but why is the mucus in the throat not coughed up?
The mucosa of the lower respiratory tract is covered with cells with hairs on the surface, between which are glands from goblet cells. This is the so-called mucociliary apparatus.
The viscous, thick, almost liquid-free mucus secreted by the previously described goblet cells is the basis of sputum. It is necessary to remove infections, allergens, decay products, dust, in general, all foreign substances from the trachea and bronchi, and the process of moving an already formed tracheobronchial secret is called mucociliary clearance. The shells of the ENT organs are literally penetrated by a capillary network, from the circulating blood of which cells that are considered immune penetrate into the sputum, so the mucus in the throat becomes an active protective component, in the literal sense of the word, destroying harmful organisms.
In the normal state, the mucous membrane produces no more than one hundred ml of protective mucus. But the volume increases significantly with the onset of inflammation or allergic processes.

An increase in viscosity, thickening of mucus is the result of the activity of irritants that come from outside or act inside the body, an increase in the concentration of monosaccharides, immune cells and proteins in it. Namely, it contributes to an increase in the density of the tracheobronchial secretion:
- imbalance of water in the body;
- dry air;
- allergy;
- trauma or burns of the mucosa;
- hyperhydrolysis;
- the use of carbonated drinks, excessively spicy, or hot / cold dishes;
- failure in the natural functioning of the ciliated epithelium;
- atrophy of the tissues of the nasopharynx, larynx;
- bacterial or viral respiratory infections.
Such sputum in the throat without coughing or even with it is poorly expectorated due to its extreme viscosity and, as a result, accumulates in the respiratory tract. In addition, sputum stagnation can lead to the development of complications: acute bronchitis or pneumonia. Therefore, it is important not to self-medicate, but to consult a doctor in time for help in thinning and expectorating sputum.
What diseases can cause mucus to accumulate in the throat?
The accumulation of mucus in the nasopharynx is possible with the following diseases:
- with pharyngitis of viral, fungal or bacterial origin;
- and also accumulates sputum in the throat with sinusitis;
- or adenoiditis.
When is it necessary to see a doctor?
As soon as there is a feeling of accumulation of sputum in the throat, it is urgent to consult a doctor. Only he is able to find out the real reasons for the increase in the concentration of sputum and its viscosity. Self-medication can be dangerous, especially if the child has a buildup of mucus.
It is also important to see a doctor for smokers who expectorate large portions of sputum in the morning.
In the morning, brown mucus accumulates in the throat - what is it?
Brown sputum usually consists of:
- mucus produced in the respiratory tract;
- saliva;
- bacteria or viruses;
- dust;
- cells of the immune system;
- decay products of the lungs;
- and blood.

Naturally, the color of sputum cannot unequivocally indicate a specific disease, but it gives reason to suspect bleeding that has occurred in the respiratory system. This is possible with the following dangerous diseases of the lungs and bronchi:
- with inflammation (pneumonia);
- with oncology (cancer);
- with tuberculosis;
- with a heart attack (occurring in the lung);
- or in acute and chronic bronchitis.
The brown mucus that smokers expectorate in the morning is a symptom of the so-called smoker's bronchitis, which is not an insignificant feature, as it is commonly read by the people, but a dangerous disease of the lungs. During the night, sputum accumulates in the bronchi, and in the morning, with the movement of the body, it irritates the reflexogenic areas and provokes a cough.
This condition is treated only after the complete cessation of active smoking.
What does accumulation of mucus in the throat after eating mean?
When mucus accumulates in the throat after eating, this may indicate the following processes in the body:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- insufficient fluid intake;
- malnutrition, for example, eating salty, spicy, spicy or sweet foods in large quantities;
- and also the cause of mucus after eating can be milk.
Such a symptom is treated by establishing a healthy diet, increasing the volume of fluid, which the doctor prescribes only after the complete exclusion of chronic tonsillitis, pharyngitis or sinusitis.
Symptoms of Mucus Accumulation in the Throat
Symptoms that indicate the accumulation of mucus in the throat are:
- sore throat, burning sensation;
- constant desire to cough;
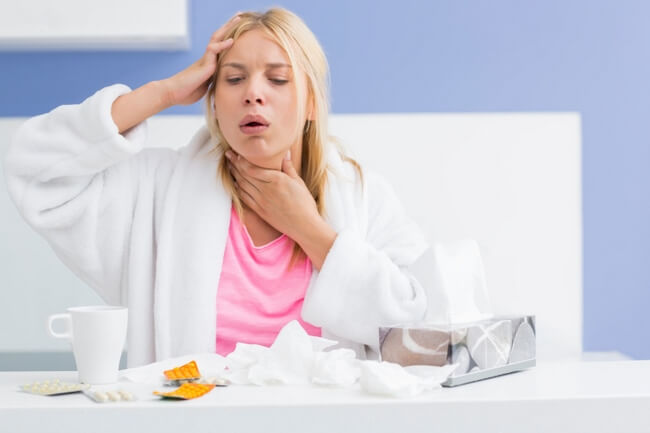

- discomfort when swallowing food, water or saliva;
- rare expectoration or swallowing of mucus clots;
- an increase in lymph nodes under the lower jaw and on the back of the head;
- headache.
Treatment
How to get rid of phlegm in the throat? First of all, you need to see a doctor.
The doctor will consider the results of sputum examination, bronchoscopy, as well as examination of the patient's oral cavity and back wall of the throat as the reason for prescribing treatment. The sputum is definitely infectious or fungal in nature in the presence of a bad smell.
Treatment in any case will be complex, but speaking of local therapy aimed at relieving discomfort in the throat, the following can be prescribed:
- Givalex;
- Ingalipt;
- Bioparox;
- Cameton;
- Oralcept.

Features of the use of sprays will depend on the diagnosis, in particular, the doctor may recommend spraying the mouth, nose and throat cavities three or four times a day for a week.
Pastilles and lozenges Septolete, Strepsils, Faringosept have a similar effect. They are used no more than 6 pieces per day after a 4-hour interval between uses.
Inhalations are often used to relieve discomfort in the throat. For steam inhalations, it is recommended to use an alkaline solution (1 teaspoon of soda per half liter of water) with a teaspoon of eucalyptus or calendula tincture; saline solution (1 teaspoon of salt per liter of water) is optimal for a nebulizer. Preparations for filling the nebulizer are selected only by a professional doctor.
An integral part of the treatment will be expectorant and sputum thinning drugs:
- mucolytics - agents that increase the fluidity of sputum without affecting its volume, there are direct and indirect effects
- mucolytics of direct action destroy chemical. compounds in the composition of the secret are presented in the form of Acetylcytein (ACC, Cofacin, Fluimucil, Mucosolvin), enzymes (Trypsin, Streptokinase, Alphachymotrypsin), Mucaltin, Ascorbic acid;
- mucolytics of indirect action reduce the production of mucus, change its composition, are presented in the form of Bromhexine, Ambroxol (Lazolvan, Ambrobene, Flavamed), Foradil, Ventolin, Theophylline, Akolate, Pulmicort, etc.
- Mucokinetics - drugs that accelerate the removal of mucus from the bronchi and throat, with the help of cough excitation (Bromhexine, Ambrobene, Bicarbonate and Sodium Ethane Sulfate.
If phlegm in the throat provokes a nose disease, you must regularly:
- do nasal lavage;
- treat nasal passages with drugs prescribed by a doctor (IRS-19, Naphthyzin, Sanorin, Knoxprey, Xilen, etc.);
- gargle more than three times a day with decoctions of medicinal herbs or medicinal solutions;
- use a humidifier;
- drink a sufficient amount of liquid per day (1.5-2 liters);
- carry out steam or nebulizer inhalations.
And also, in addition, the doctor may prescribe physiotherapeutic methods of treatment or puncture.
How to get rid of the sensation of a lump in the throat?
The condition when it is difficult to swallow, speak, breathe, associated with the feeling of the presence of a large mucous coma in the throat, is commonly called a “lump in the throat”.
Indeed, this state is not very pleasant, it wants to be eliminated immediately. How to get rid of a lump in your throat as soon as possible:
- Conduct alkaline steam inhalation (with soda), it will make it easier to cough up a lump;
- While the inhalation is being prepared, you can rinse your throat with a weak soda or saline solution (dissolve half a teaspoon of soda or salt in a glass of water);
- Or drink a glass of alkaline mineral water if swallowing is easy.

It is better not to swallow the sputum that has come off after these manipulations, but to spit it out. If the spitted lump has an unpleasant, putrid odor, it is urgent to inform the otolaryngologist about this and diagnose the upper respiratory tract as soon as possible, since this may indicate a bacterial lesion.
And also the sensation of a “lump in the throat” can occur with a trauma to the larynx, which resulted in suppuration of the tissues of the larynx and their swelling. A similar situation also needs an urgent consultation with an ENT doctor, because only he will be able to assess the patient's condition and remove, if necessary, the remnants of traumatic particles.









Aromatherapy - Essential oils: table of properties and uses
Cleansing the energy of the apartment with a church candle
Essential oils for aromatherapy: properties, uses and contraindications
Weakness in the body and drowsiness: causes in adults
How to clean an apartment from negativity with a church candle