Sleep Apnea (Obstructive Apnea; Central Apnea; Mixed Apnea)
Description of sleep apnea
Sleep apnea is a condition in which breathing is interrupted repeatedly during sleep. The period of time during which breathing stops or decreases typically ranges between 10 and 30 seconds. With frequent episodes, sleep apnea can seriously impair the quality of sleep.
Causes of sleep apnea
There are three types of sleep apnea that occur for various reasons:
- Obstructive sleep apnea - as a result of temporary, partial or complete blockage of the airways;
- Central apnea - as a result of a temporary stoppage of breathing (cessation of the functioning of the respiratory system);
- Mixed sleep apnea is a combination of the first two types of sleep apnea.
Sleep apnea risk factors
Factors that may increase the risk of sleep apnea include:
- Gender: male;
- Overweight;
- Large neck circumference;
- Age: middle and old age;
- family history of sleep apnea;
- Structural abnormalities in the nose, throat, or other part of the airways:
- polyps;
- Enlarged tonsils;
- The slope of the nasal septum;
- Hypothyroidism;
- Medicines: taking sedative and hypnotic drugs;
- Smoking.
Sleep apnea symptoms
Sleep apnea symptoms may include:
- Tiredness and drowsiness while awake;
- Loud snoring;
- Breathing stops during the night;
- Frequent waking up at night;
- morning headache;
- poor concentration or memory problems;
- Irritability or irascibility.
People with chronic, untreated sleep apnea may be at risk for:
- traffic accidents;
- depression;
- Diseases of the heart.
Sleep Apnea Diagnosis
A sleep study is used to diagnose sleep apnea.
Night sleep study - Polysomnography
An overnight sleep study helps determine the presence and severity of sleep apnea. During sleep, the following is measured:
- Eye and muscle movements;
- Brain activity (electroencephalogram);
- Heart rate;
- Breathing (frequency and depth);
- The percentage of saturation of red blood cells with oxygen.
Other studies in sleep apnea
In addition to polysomnography, the doctor may prescribe:
- Blood tests (for example, to check thyroid function);
Sleep Apnea Treatment
There are several treatment options for sleep apnea, including:
Behavioral Therapy
- Need to lose weight if you are overweight;
- Avoid the use of sedatives, sleeping pills, alcohol and nicotine. They may worsen the disorder;
- Try sleeping on your side instead of your back;
- Place the pillow in such a way that it is as comfortable as possible to sleep;
- If you experience daytime sleepiness, practice safety measures, such as not driving or operating potentially dangerous machinery.
Mechanical sleep apnea therapy
Sleep apnea is treated with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP). For these purposes, a mask is used, which is worn over the nose and / or mouth during sleep. The ventilator maintains a sufficiently constant and continuous flow of air through the airway to prevent tissue destruction and airway blockage. In some cases, dental instruments are used to help hold the tongue or jaws open.
Surgery to treat sleep apnea
Types of surgery that can be done to treat severe cases of sleep apnea include:
- Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty - the doctor removes excess soft tissue from the nose and / or pharynx;
- Bimaxillary surgery - the jaw bone moves forward;
- Tracheotomy - In life-threatening cases of sleep apnea, a hole is made in the trachea into which a breathing tube is inserted. This allows for normal breathing;
Bariatric surgery can help with weight loss in some people who are obese. This surgery can reduce many of the complications associated with obesity, including sleep apnea.
Taking medications for sleep apnea
Used only in the treatment of central sleep apnea. Acetazolamide (Diamox) may improve the ability to regulate breathing. Overall, there is not much evidence to support the use medicines for the treatment of sleep apnea.
If the level of oxygen in the blood drops too low even after opening the airways, treatment can be given by supplying supplemental oxygen to the lungs.
Prevention of sleep apnea
You can prevent sleep apnea by maintaining a healthy weight. Avoid alcohol, nicotine, and sedatives, which can lead to airway obstruction.
Sleep apnea syndrome is manifested by frequent pauses in breathing during sleep, causes a number of unpleasant symptoms and can provoke serious complications.
If you suspect sleep apnea Definitely need to see a somnologist!
Why do you stop breathing in your sleep?
Sleep apnea syndrome occurs in people different ages most often in patients older than 40-50 years. The disease occurs in two main forms: obstructive and central. In the vast majority of cases, sleep apnea is obstructive (stopping breathing due to snoring).
The development of obstructive sleep apnea is based on the periodic collapse (overlapping of the lumen) of the upper respiratory tract, due to which respiratory arrests occur. The fact is that patients with sleep apnea have initial disorders and features due to which their pharynx narrows. During sleep, when the muscles of the body relax, the narrowing of the pharynx is aggravated. Its walls begin to touch, vibrate when inhaling and exhaling, creating the sound of snoring. Occasionally, the walls completely collapse, interrupting breathing.
At central apnea sleep, there are also pauses in breathing, but without snoring.
During the night, a person can have 400-500 such pauses lasting from 10 seconds to a minute or more.
Causes of Obstructive Sleep Apnea
 The most common causes of obstructive sleep apnea are:
The most common causes of obstructive sleep apnea are:
- Overweight. With excess weight, fat accumulates between the structures of the neck and squeezes the pharynx, narrowing its lumen.
- Age (apnea is more common in the elderly due to general muscle weakness).
- Floor. Sleep apnea syndrome usually occurs in men, which is associated with the distribution of adipose tissue and the anatomical structure of the pharynx.
- The use of alcohol, and narcotic drugs that cause weakness of the muscles of the nasopharynx and oropharynx.
- Menopause. Hormonal changes cause excessive relaxation of the muscles of the respiratory tract and the entire body.
- Reduced lower jaw. With this feature of the structure, the anterior-posterior size of the lumen of the pharynx decreases.
- Excess tissue of the soft palate, enlarged palatine tonsils. They directly block breathing.
- Smoking. Sleep apnea is more common in smokers than in non-smokers.
Obstructive sleep apnea symptoms
Sleep apnea is interrupted, restless sleep. When breathing stops and the level of oxygen in the blood drops critically, alarm signals begin to enter the nervous system. They cause an incomplete awakening of the brain: a person does not wake up completely, but the nervous system takes control of the muscles and restores normal breathing. As sleep deepens, the cycle repeats again. As a result, the whole night of the patient consists of a series of attacks of suffocation and micro-awakenings. The structure of sleep is disturbed, it becomes intermittent, does not give a feeling of cheerfulness.
Sleep apnea syndrome provokes morning headaches, weakness, irritability, drowsiness during the day, increased fatigue, decreased concentration, anxiety, or even depression. Uncontrolled spontaneous falling asleep throughout the day causes accidents at work or while driving.
There are other symptoms of sleep apnea: nocturnal heart rhythm disturbances, a steady increase in blood pressure, sweating, frequent urination at night.
Gradually, the apnea syndrome causes severe arterial hypertension with frequent hypertensive crises, accelerated development of coronary disease. It increases the risk of stroke and myocardial infarction, especially at night and in the morning.
Watch this video: a patient talks about the symptoms he experienced before he started treatment for sleep apnea. Do you have similar symptoms?
Dangerous facts about sleep apnea
On this page you can go. If, according to the results, you find that you have a high probability of this disease, we recommend that you contact a somnologist, because snoring with pauses in breathing during sleep is extremely dangerous for health.
Consider:
- With a severe degree of apnea, a person may not breathe in total for up to 4-5 hours per night;
- Respiratory arrests cause a slowdown in the activity of the heart up to its complete stop for 3-10 seconds;
- cases sudden death in a dream in many cases are caused precisely by the fact that a person had a sleep apnea syndrome;
- Since the disease strikes different systems organs, patients often visit urologists, therapists, cardiologists, neurologists, psychologists for years without effect, although in fact all problems are due to the presence of sleep apnea.
Sleep apnea is a good reason to see a doctor immediately!
Sleep apnea is a temporary pause in breathing that occurs periodically during sleep. Pathology is accompanied by general fatigue, apathy and decreased performance, which causes a lot of discomfort and interferes with a productive lifestyle.
Apnea - what is it?
What is sleep apnea and how does it manifest itself? Apnea is a disease, it is pathological and requires complex treatment depending on the form and severity.
Classification of apnea according to the mechanism of respiratory arrest:

The following types of stops are distinguished by the duration:
- Hypopnea - oxygen deficiency is up to 50%, the paths are partially blocked (only part of the diaphragm moves, breathing is rapid);
- Sleep apnea, which is characterized by complete relaxation of the larynx. The delay lasts more than 10 seconds.
To determine the severity, pay attention to the duration and frequency of the phenomenon:
- Mild form - 5–20 attacks per night.
- The average form is 20–40 attacks.
- Severe form - more than 40 stops.
Less than five episodes per night is considered safe for a person.
The level of apnea is calculated using a formula that takes into account these indicators and the duration of stops in seconds that occur during the hour of rest.
Symptoms
The main symptom of sleep apnea is a sudden interruption of breathing during sleep, frequent awakenings, restless sleep and heavy snoring (stops abruptly before breathing stops). The patient often does not remember the night episodes, so others - children, parents or a significant other - can indicate deviations. Accompanying signs should alert:

These signs are temporary. They are mainly observed at night and in the morning, and disappear in the evening. If treatment is not started on time, the general condition of the person worsens and other deviations develop:
- sexual dysfunction and prostatitis (in men);
- a sharp set of body weight;
- arrhythmia;
- cardiovascular diseases.
In 50% of patients, comorbidities are diagnosed that significantly worsen the course of apnea. Treatment in this case is aimed at eliminating arterial hypertension, bronchial asthma, coronary heart disease, and other lung diseases.
It is also very important to supervise children during the day and at night. Breathing through the mouth, urinary incontinence, increased sweating, slow reaction, a sharp change in temperament and unusual postures during sleep can give out pathology.
Causes
The main cause of sleep apnea is a violation of the motor function of the muscles and tissues of the larynx. Relaxation of this part of the body leads to interruptions in the supply of oxygen to the lungs, from which the person begins to suffocate and wakes up.
In most cases, anoe is a congenital pathology that is inherited from parents.
In addition to genetics, there are a number of features of the body and bad habits that lead to the development and aggravation of the condition:

Being overweight is the most common cause, especially if a person has fatty tissue in the neck, chin, and abdomen. Accumulations of fat put pressure on the muscles in these areas, preventing the diaphragm and larynx from working properly. Excess weight tends to be deposited in these places in men, so they suffer from sleep apnea more often.
Damage to peripheral nerves and hypofunction of the thyroid gland also lead to a decrease in muscle tone.
Prevention
Compliance with the rules below will help reduce the manifestations, and in some cases even completely cure sleep apnea:

In addition, it is important to provide the most comfortable conditions and peace: exclude all unnecessary sounds, give up the TV and computer before going to bed, use a dark blindfold.
Treatment
The method of therapy directly depends on what type of apnea is diagnosed. First of all, the treatment of apnea should be aimed at eliminating the causes, therefore, therapy for the central nervous system, obesity, diabetes mellitus, etc. is needed.
With mild obstructive sleep apnea, the cause of which is anatomical features, surgical intervention is prescribed. The attending physician prescribes a method of therapy after a complete diagnosis.
In the moderate and severe form, surgery is ineffective, since a mechanical obstruction is not the main hazard. How to treat? In this case, CPAP, BiPAP and TRIPAP devices are used. 
Surgery
It is prescribed for enlarged tonsils, curvature of the lower jaw and nose. Includes the following types of operations:
- The application of the Pillar system is the introduction of synthetic plates into the soft palate, which make it stiffer and support it like a framework. Effectively eliminates snoring.
- Adenomectomy - removal of hypertrophied lymphoid tissue. Polyps are removed on the upper part of the nasopharynx under local anesthesia.
- Tracheostomy - opening the trachea and inserting a special tube that provides constant access to air, even when the path to breathing is completely blocked.
- Bariatrics. It is carried out with severe obesity and is a surgical reduction in the size of the stomach. A person begins to consume less food and loses weight.
- Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty - removal of part of the soft palate.
- Tonsillectomy - removal of hypertrophied tonsils.
CPAP
This is one of the best and safest ways, which consists in connecting a special mask that covers the nose and mouth before going to bed.
Through a special tube under pressure, air enters, providing a constant supply of oxygen to the body. Modern devices have special settings for humidity and air temperature, which allows you to create the most comfortable conditions for the patient.
An effective treatment for sleep apnea caused by tongue-throwing is the placement of rubber mandibular splints on the teeth to help hold the jaw and tongue in a secure position.
When diagnosing the central form, along with the main treatment, the diuretic Acetazolamide is used, which relieves swelling and improves blood supply to the brain cells.
Complications
 In the absence of treatment, a person goes into a state that threatens his life. Loss of coordination and fatigue can lead to dangerous situations like getting into an accident.
In the absence of treatment, a person goes into a state that threatens his life. Loss of coordination and fatigue can lead to dangerous situations like getting into an accident.
Constant oxygen starvation increases the risk of heart attack and stroke by 30-40%. In severe forms, sleep apnea enters a daytime phase, and carbon dioxide metabolism is disrupted 24 hours a day. In such cases, the diagnosis of "Pickwick syndrome" is established, when, due to drowsiness and general fatigue, a person can fall asleep at any time and in any place, which is fraught with physical and industrial injuries.
The rapid increase in clinical manifestations can lead to disability and even death.
The term sleep apnea refers to a condition in which ventilation of the lungs stops during sleep. and this stop lasts approximately 10 seconds.
Sleep apnea: causes
The duration of apnea reaches both 30 seconds and 2 minutes in severe cases.
Kinds:
- obstructive
- central apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea is a condition in which a person's upper airways narrow or close during sleep. The uplift of the chest is maintained simultaneously with the cessation of breathing. Accompanied by apnea with deep breaths and weak.
Causes of obstructive sleep apnea:
- Difficulty in the passage of air into the upper respiratory tract with weakening of the muscles of the pharynx and tongue. Control over these muscle groups is retained by special parts of the brain, which can be impaired due to anomalies that narrow the radii of the upper respiratory tract: a violation of the location of the hyoid bones, the presence of adenoids, changes in the tonsils (inflammation), diseases of the lymph nodes, the presence of tumors or cysts, the spread of edematous-inflammatory processes.
- Difficulty in the passage of air into the upper respiratory tract with.
- Difficulty passing air into the upper respiratory tract when taking tranquilizers or alcohol.
- Difficulty in the passage of air into the upper respiratory tract is observed in elderly people.
- Central sleep apnea is a condition in which a person suffocates while sleeping. The heaving of the chest does not occur with the simultaneous cessation of breathing. Apnea is accompanied by nocturnal awakenings and daytime sleepiness.

Causes of central apnea:
- Difficulty breathing in chest muscles. Control over these muscle groups is maintained by special parts of the brain, which can be disturbed due to anomalies caused by traumatic brain injuries, inflammatory processes, and organic lesions.
- Difficulty in breathing movements of the chest muscles as insufficiency of the respiratory center. Violation of the saturation of the body with oxygen, associated with the problem of transporting gases between the lungs, tissues and cells of the body. Agnosia is observed with or a change in blood saturation with hemoglobin, that is, a restriction of enzymes at the cellular level.
The causes of obstructive and central sleep apnea are similar and depend on the normalization of the functions of the muscle groups responsible for certain breathing processes. Injuries, inflammatory processes and other disturbances in the functioning of the body lead to sleep apnea.
Sleep apnea in children
Sleeping children are prone to brief respiratory arrest and it is extremely dangerous for them. Such a condition in a child is not uncommon, and is associated with the immaturity of the mechanisms responsible for the normalization respiratory center. Apnea threatens premature babies, newborn babies and children with catarrhal inflammation, hematomas of the upper respiratory tract and.
The presence of spontaneous sleep apnea in newborns and infants with an incompletely developed central nervous system is also facilitated by a violation of heat metabolism or overheating.
In newborns, both central and obstructive (mixed) spontaneous sleep apnea syndromes are manifested.
For healthy babies, holding their breath for 15 seconds is a common occurrence. If this happens, it is necessary to touch the child with a gentle touch, to do sternum or artificial respiration. He will start and breathing will resume.
If the baby has sleep apnea, do not be upset, children outgrow this condition and the body is rebuilt. To alleviate apnea, the room must be ventilated, the baby should not be overheated and put to bed without a pillow (first year).
If you notice your child has sleep apnea, note the frequency of the event and the duration of the cessation of breathing. Agnosia is accompanied by pallor, slow heartbeat, blue lips and fingers, reflex muscle contraction, loss of consciousness.
Discuss concerns with your pediatrician. Apnea leads to serious violations in the behavior of the baby, in developmental deviation. Your doctor will help you find a solution. Otherwise, the consequences may be irreversible or the outcome may be fatal.
Sleep apnea in children is no exception. If your baby has a similar problem, you need to be well informed about it.
For more information about sleep apnea in a child, we invite you to learn from the proposed video.
Sleep apnea: symptoms
Sleep apnea comorbidities:
- hypoxemia
- sleep fragmentation
Hypoxemia - a decrease in the amount of oxygen required in human blood plasma due to circulatory disorders, an emergency need for oxygen in tissues (excessive muscle load), a decrease in gas exchange in the pulmonary capillaries in their diseases, a drop in the content of hemoglobin in the blood plasma ().
If sleep apnea lasts for 15 seconds, hypoxemia occurs. The brain of a person who has fallen into a state of apnea must regulate the state that has arisen. In other words, with a reduced or insufficient concentration of oxygen in the composition of human blood, the brain must transfer the body to another, more high point(phase) of sleep, in which muscle tone will increase and air availability will be restored. The sufferer will snort loudly with a sigh and the tension will subside.
In patients, sleep apnea occurs in repetitions, fragmentarily throughout the entire segment of the night. The mind sinks into deeper sleep points and emerges.
A similar situation knocks down the deep and superficial stages of sleep in the body, affecting the level mental ability, reducing memory and depressing the patient's condition as a whole. In the morning, there is high blood pressure, there is a rapid heartbeat or a complete stop in the middle of the night or in the morning.

In patients with sleep apnea, growth hormone secretion is impaired, weight gain, cardiac hormone synthesis is impaired, heart rate and release are reduced, which leads to impaired stimulation of hemostasis phases and the formation of a red blood clot. In patients with sleep apnea, due to a decrease in testosterone synthesis, sexual activity decreases.
The symptoms of sleep apnea sufferers can be described as follows:
- Complaints of prolonged lethargy, extreme drowsiness. The patient wants to sleep from time to time, he naps while sitting, falls asleep at work.
- Complaints of migraines during the day and headaches in the morning. Migraines are accompanied by pain in the neck and neck.
- Complaints about failures in . A person does not remember what and when he did, deja vu is noted.
- Complaints of irritability and extreme emotionality. The patient quickly loses his temper, the irritant is not noticed.
- Complaints about the muscles in the legs. The patient has broken bones and there is tension in the muscles.
- Complaints of decreased libido and lack of sexual activity. The person is oppressed and capricious.
Sleep apnea is a dangerous condition that leads to a number of serious diseases.
Diagnostics
In addition to the complaints of those suffering from apnea, there were complaints from relatives and friends:
- constant snoring and no breathing
- talking in a dream
- frequent awakening during the night
- grinding
- frequent trips to the toilet during the night
In recognizing sleep apnea, contact with the patient's relatives and friends is necessary and their presence in setting the precedent for not breathing during sleep.
In the practice of an outpatient clinic for diagnosis, the method of Professor Rovinsky is used, where several relatives of the patient during his sleep note the duration of pauses and the time of cessation of breathing with a stopwatch.
An external examination determines the weight and degree of obesity in patients, the diameter of the neck and blood pressure.
Patients with sleep apnea are assigned consultations of specialists in the field of otolaryngology to identify pathologies of the ENT organs. Often found chronic rhinitis and purulent, curvature of the cartilage of the nasal septum, acute tonsillitis.
Diagnosis of the nasopharynx is additionally carried out using a flexible device-fibroendoscope. Pharyngoscopy will help the doctor examine the pharynx, laryngoscopy - the larynx through the oral cavity and rhinoscopy - the nasal cavity.
Reliable and complete picture the presence or development of apnea establishes a long (8-hour) night polysomnographic study. The study includes the fixation of electrical impulses of the brain (ECG, EEG) and at the same time respiratory activity (passage of air through the mouth and nose, respiratory actions of the muscles of the peritoneum and sternum, saturation of blood plasma with oxygen, the presence of snoring, body position in sleep).
Polysomnographic analysis reveals the duration and number of sleep apnea phases and the changes that take place.
In order to timely and correctly select the methods of treatment, it is important to determine the nature and cause of the manifestation of apnea, and without a diagnosis it is difficult to do so.
Sleep apnea treatment
Treatment of sleep apnea includes the use of various methods, affecting the cause of the disease:
- non-drug
- medicinal
- operational
- Sleep with your head slightly elevated. Either a low pillow or a bed with a raised edge (20 cm higher) will do. Avoid sleeping in the supine position.
- Bury Galazolin drops at night to prevent nasal breathing, gargle with a solution.
- During sleep, use oral appliances to help maintain the passage of air to the respiratory tract.
- Treat diseases of the upper respiratory tract (chronic rhinitis, purulent sinusitis). Avoid sleeping pills and alcoholic drinks, reduce weight.
- Use technical CPAP (ventilation) therapy to help maintain a constant positive airway pressure, and to improve breathing during sleep and improve the condition of patients during the day. The method is the most promising and effective of the existing ones.
- Purpose medication Theophylline - a way of salvation for patients with obstructive sleep apnea and Acetazolamide - for patients with central.
- In some cases, there is no unnecessary correction of the nasal cartilage, which completely eliminates the causes of sleep apnea syndrome. Operations to cauterize the upper palate are carried out with extremely severe anomalies.
The increase and duration of manifestations of sleep apnea occurs over time and is accompanied by severe disability or death. Timely treatment will help to avoid unwanted consequences.

Prevention
Prevention of sleep apnea complications is not specific and calls for the need to intervene in the treatment of all kinds of related specialists: a neurologist, a cardiologist, an otolaryngologist and a pulmonologist.
Prevention consists of weight loss, avoidance of alcohol, sleeping pills, elimination of pathologies of the nasopharynx, treatment of ENT deviations and observation of concomitant background diseases.
If you have trouble sleeping, try these suggestions:
- Give up nicotine and alcoholic beverages
- Sleep on a firm mattress, low pillow, and constantly change your sleeping position
- Take a few drops of salt water in the evening
- During the day, do exercises, warm-up, stretching, however, before going to bed, refrain from active activities.
- The rest room should not have a source of noise or an extra source of light
Compliance with a number of rules below will help to avoid respiratory arrest:
- Try to sleep on your side, on an elastic feather bed, without a pillow, in a ventilated room
- Sleeping clothes should be loose and open
- Try to take regular walks or warm-ups on fresh air
For the prevention of sleep apnea in babies, it is suitable:
- Regular ventilation of the room. The kid should constantly be in the fresh air, both on the street and at home.
- Wrapping up a child is strictly undesirable.
- Laying the baby up to a year of life without a pillow.
- Fight against diseases. If the baby is not sick, prevention will not be superfluous.
- Breastfeeding and sleeping baby in the room with mother.
Parents should remember that normally, a baby’s breathing can be both accelerated and slowed down, and in a healthy child up to a year, both respiratory arrest and an uneven rhythm are acceptable.
Sleep apnea is not a harmless disorder or disorder of the body. Apnea requires monitoring, treatment and prevention.

 Sleep apnea In medicine, it is commonly referred to as obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. But for common man it's much easier to say "sleep apnea". Therefore, later in the article I will call this syndrome so as not to clog the text with unnecessary medical terms. In my previous article, I talked about the physiology of sleep and the relationship of endocrinology with sleep. In this article, we will talk, as promised, about sleep disorders associated with obesity.
Sleep apnea In medicine, it is commonly referred to as obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. But for common man it's much easier to say "sleep apnea". Therefore, later in the article I will call this syndrome so as not to clog the text with unnecessary medical terms. In my previous article, I talked about the physiology of sleep and the relationship of endocrinology with sleep. In this article, we will talk, as promised, about sleep disorders associated with obesity.
You probably think that sleep apnea is a disease that is not necessary to talk about, but I want to convince you that this is not so. Read to the end and you will know a lot more about sleep apnea syndrome.
What is sleep apnea
Sleep apnea is a condition characterized by repeated episodes of obstruction (blockage) of the airways during sleep, in which the level of oxygen saturation of the blood decreases, i.e., hypoxia occurs. In other words, in a dream, a person stops breathing. To talk about the pathology of breathing with, I will briefly explain how a person breathes during normal sleep.
In general, irregular breathing during sleep is the norm in healthy person. For example, during falling asleep or during REM sleep, a person may experience unstable breathing (rapid breathing), which is replaced by complete or incomplete breathing stops. The duration of such “physiological” respiratory disorders is normally from 10 to 40 seconds, and cessation of breathing for less than 10 seconds is not considered at all for sleep apnea.
To determine the norm or pathology of respiratory disorders, the apnea index is used, which consists in counting episodes of respiratory arrest per hour of sleep. Currently, an apnea index equal to or greater than 5 episodes per hour is considered pathological.
How common is this pathology? Currently, there are no Russian statistics, since in our country there is an extremely low number of centers specializing in the diagnosis of sleep disorders, as well as a shortage of somnologists. But there are few statistics in the world that indicate that men have this problem more often than women (6-8:1). In addition, it has been proven that among patients with obesity, sleep apnea occurs more by 55% than in the general population.
Sleep apnea clinic
The most common symptom of this pathology is snoring during sleep.
Snoring is a sound phenomenon that occurs when the walls of the pharynx, tongue, arches and soft palate vibrate at a certain frequency.
Recently, ENT doctors have been asked to call any occurring during sleepsounds that come from the upper respiratory tract. Snoring most often occurs during sleep. open mouth. When inhaling, the palatine curtain is separated from the tongue to the back of the pharynx, which is accompanied by decompression of the oral cavity with a characteristic sound.
The main factor in the collapse of the upper respiratory tract is a decrease in the tone of the muscles of the pharynx when falling asleep. In this case, the configuration of the pharyngeal section of the upper respiratory tract changes and turbulent flows of inhaled air arise, which turn into snoring.
How is snoring different in obese patients with sleep apnea? Snoring is usually loud, very often patients themselves report that they hear their own snoring or wake up from it. But of course, much more often snoring worries relatives and friends of snorers. If you watch such a sleeping snoring person, you will notice that snoring is periodically interrupted by periods of silence, which can last tens of seconds. No sounds are heard, but the chest and abdomen continue to rise and fall as if breathing.
Chaotic movements of the limbs can occur, and so powerful that they can deliver quite tangible blows to those sleeping nearby. At the end of the episode, a loud snoring follows, some say: “Like a pipe burst”, after which breathing is restored, and snoring continues. Those same periods of silence correspond to episodes of sleep apnea.

When the walls of the respiratory tract collapse, the supply of oxygen stops and the level of saturation with it falls, and the level of CO2 rises. The increasing concentration of CO2 in the blood is a powerful stimulus for the central nervous system, which excites it and leads to complete awakening or only to the appearance of activation on the EEG. After that, muscle tone is restored, the lumen opens, and air enters the lungs again. And the dream, meanwhile, deepens again, and everything will repeat itself.
The described episodes of sleep apnea can be repeated in a patient up to hundreds of times a night and become the reason for going to the doctor, most often at the insistence of concerned relatives. Snorers themselves in most cases are unaware of their problem, and only 30% of them report periodic awakenings from lack of air.
Based on this syndrome, other complaints arise: dissatisfaction with night sleep and daytime sleepiness. According to studies, sleepiness during the day is noted by up to 90% of respondents. Sometimes daytime sleepiness is imperative. Drowsiness is often accompanied by difficulty concentrating and remembering. There are episodes of automatic behavior when routine work is performed semi-automatically.
Drowsiness is of particular importance for motorists. Another study shows that car accidents are much more likely to happen to people suffering from sleep apnea.
Due to frequent awakenings, there is a decrease in the representation of deep sleep, as well as the effect of hypoxia on the brain, which leads to intellectual and emotional disorders. Clinically, this manifests itself:
- irritability
- anxiety
- outbursts of aggression
- depressive states
In addition, patients with sleep apnea syndrome note:
- dry mouth upon waking
- headaches in the morning, probably caused by brain hypoxia
- frequent urination (nocturia) and urinary incontinence (enuresis)
- heartburn, which may occur due to gastric reflux provoked by changes in intra-abdominal pressure
- excessive sweating, experienced by more than 60% of patients
Endocrine disorders in sleep apnea syndrome
As I said in my previous article, sleep and hormone secretion are very closely related. Due to the fact that chronic sleep deprivation occurs in this disease, the secretion of the main hormones is also disturbed. First of all, it concerns the growth hormone - pituitary somatotropic hormone (GH). During the research, the disappearance of the nocturnal peak of the secretion of this hormone was observed against the background of a decrease in the representation of the slow-wave sleep phase (delta sleep). But as soon as normal sleep was restored, the nocturnal peak of GH secretion was also restored.
And as I said, growth hormone is very important not only for a child's body, but also for an adult, since it is the main anabolic hormone of the body. As a result of its deficiency in children, the growth of bones and muscles is disturbed, and adults experience a decrease in efficiency, weight gain, fatigue, and a decrease in muscle strength. This is not the whole list of problems that arise with a deficiency of growth hormone. Perhaps I will somehow tell you about that amazing hormone as part of an "elective", so I recommend that you do not miss it.
In addition, constant sleep apnea leads to stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system with the release of catecholamines (adrenaline, norepinephrine). Activation of this system can contribute to the development of vegetovascular dystonia or hypertension.
Influence noted this syndrome on the production of testosterone - the main hormone that makes a man a man. With frequent sleep apnea, there is a decrease in the synthesis and production of testosterone, and the degree of decrease is directly dependent on the severity of the disease and does not depend on age and weight. However, successful treatment of the underlying disease leads to the restoration of testosterone levels. That is why, in the presence of respiratory disorders in childhood puberty is delayed.
Violations of the secretion of cortisol, glucagon, T4 and thyroxine-binding globulin in this disease have not been identified. Influences respiratory disorderson the synthesis and secretion of insulin was also not detected. The hyperinsulinemia found in the examined patients may be caused, rather, by obesity, because as a result of the elimination of apnea, the normalization of insulin and glucose concentrations did not occur.
Complications of sleep apnea
Numerous studies prove a pronounced activation of the sympathetic nervous system. Therefore, in this disease, the main target organs are organs of the cardiovascular system. Approximately 40-90% of patients suffer from hypertension. At the same time, hypertension in such people has characteristics: often only diastolic pressure ("lower" pressure) rises, but it is very difficult to treat, the pressure often rises in the morning and decreases in the evening.
Due to sympathetic activity, disturbances in the electrical stability of the heart occur, which is manifested by the development various kinds arrhythmias. The risk of myocardial infarction and stroke increases by 2-3 times.
Another complication that accompanies sleep apnea is pulmonary hypertension. Pulmonary hypertension develops in 20% of patients.
How is sleep apnea treated?
CPAP therapy
Currently, the method of choice in the treatment of sleep apnea is the use of CPAP therapy. CPAP is a treatment by creating continuous air pressure in the upper airways. This is a type of assisted ventilation of the lungs with the creation of continuous positive air pressure in the airways.
The CPAP device is a compact compressor with a flexible hose that provides a constant supply of room air at low pressure into a mask on the patient's face. Already in the first nights of treatment, obvious improvements are noted: snoring disappears, increased physical activity, endless getting up to the toilet. In the morning, patients no longer experience headaches, and drowsiness during the day is significantly reduced.
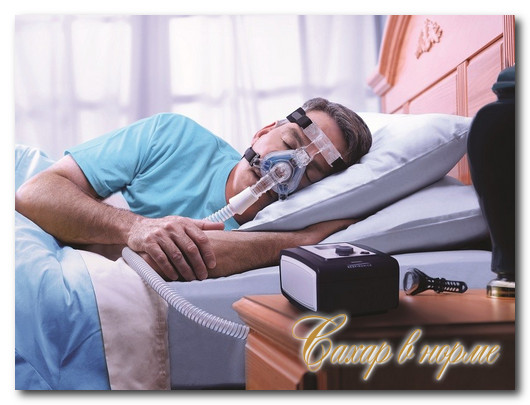
Further use of the device leads to the disappearance of other manifestations of sleep apnea syndrome. Memory and attention improve, the severity of anxiety and depression decreases, sexual desire appears. Some authors note a decrease in blood pressure.
This improvement persists for 2 weeks after stopping treatment. Thus, it takes more long-term treatment to regress all pathological conditions. In order to individually select the therapeutic air pressure, pressure titration is required in the conditions of a somnological laboratory. As a rule, one night is enough for this, after which a person purchases a device in a medical equipment store and begins to use it. Evaluate the effect of treatment after 6-12 months on polysomnography and MRI. The regression of this syndrome during treatment is explained by a decrease in swelling of the tissues of the pharynx and an increase in its lumen.
Surgery
To achieve a lasting effect of eliminating apnea, an UPFP operation is performed - uvulopalatopharyngoplasty. At the same time, a part of the soft palate with the uvula is excised and the palatine tonsils are removed, followed by suturing that tightens the back wall of the pharynx.
The indications for this operation are:
- elongated soft palate
- overgrowth of the walls of the pharynx
- tonsil hypertrophy
Medicinal treatments
Currently, medicinal methods are recognized as ineffective. Given that progesterone has a beneficial effect on breathing, doctors have tried to treat the disease with it, but data on effectiveness are conflicting, and men often developed impotence. The reduction in the frequency of apnea episodes was achieved by the use of antidepressants. Studies are currently underway to treat sleep apnea with fluoxetine and paroxetine, serotonin reuptake inhibitors.
Other treatments
Other methods include special orthodontic appliances, such as mandibular thrusters or tongue retainers. Usage such funds requires careful adjustment with the participation of orthodontists.
Taking into account the known factors that contribute to the development of respiratory failure during sleep, it is recommended to apply the "harm limitation" methodology, which includes recommendations to exclude the use of alcohol, hypnotics and sedatives, smoking cessation, refusal to sleep on the back (sew a tennis ball into the pocket on the back ). But the most effective of the "harm reduction" techniques is because there is an inextricable link between obesity and sleep apnea.
That's all for me. I'm not saying goodbye to you, as articles about other sleep disorders in obesity await you.










At what sub-zero temperature do yeast die?
Do you know how to choose the right ripe, sweet melon?
The most beautiful surnames for girls
The rarest surnames: is yours on this interesting list?
Medicinal properties and contraindications of spices and oil of oregano Oregano in cooking